Enhance Your Vision and Cognitive Function: The Unexpected Advantages of Eye Supplements Containing Lutein and Zeaxanthin
Written by Susan Parker | Updated on May 28, 2025
Reviewed by Susan Parker
Key Takeaways
Lutein and zeaxanthin enhance eye and brain health.
Nutrients filter blue light and improve cognitive function.
Sources include green vegetables, egg yolks, and supplements.
Lutein and zeaxanthin support vision and reduce eye strain.
Supplementation helps protect eyes and benefits overall health.
Carotenoids promote cognitive function and brain health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Key Takeaways
Lutein and zeaxanthin enhance eye and brain health.
Nutrients filter blue light and improve cognitive function.
Sources include green vegetables, egg yolks, and supplements.
Lutein and zeaxanthin support vision and reduce eye strain.
Supplementation helps protect eyes and benefits overall health.
Carotenoids promote cognitive function and brain health.
Frequently Asked Questions
In today's world, where we are constantly exposed to blue light from screens and noticing a decline in memory as we age, two nutrients emerge as potential heroes that could assist us in addressing these challenges.
It is truly remarkable to consider that two basic nutrients, lutein and zeaxanthin, present in green vegetables and egg yolks, possess the ability to protect your eyesight and enhance your memory.
These powerful antioxidant carotenoids not only improve vision but are also concentrated in both the eyes and the brain, where they play a critical role in promoting cognitive health. From blocking out harmful blue light to boosting reaction times, lutein and zeaxanthin provide protection and enhanced functionality for both your eyes and brain. Learn about how these nutrients work and why they could be crucial for maintaining sharp mental acuity and clear vision as you age.
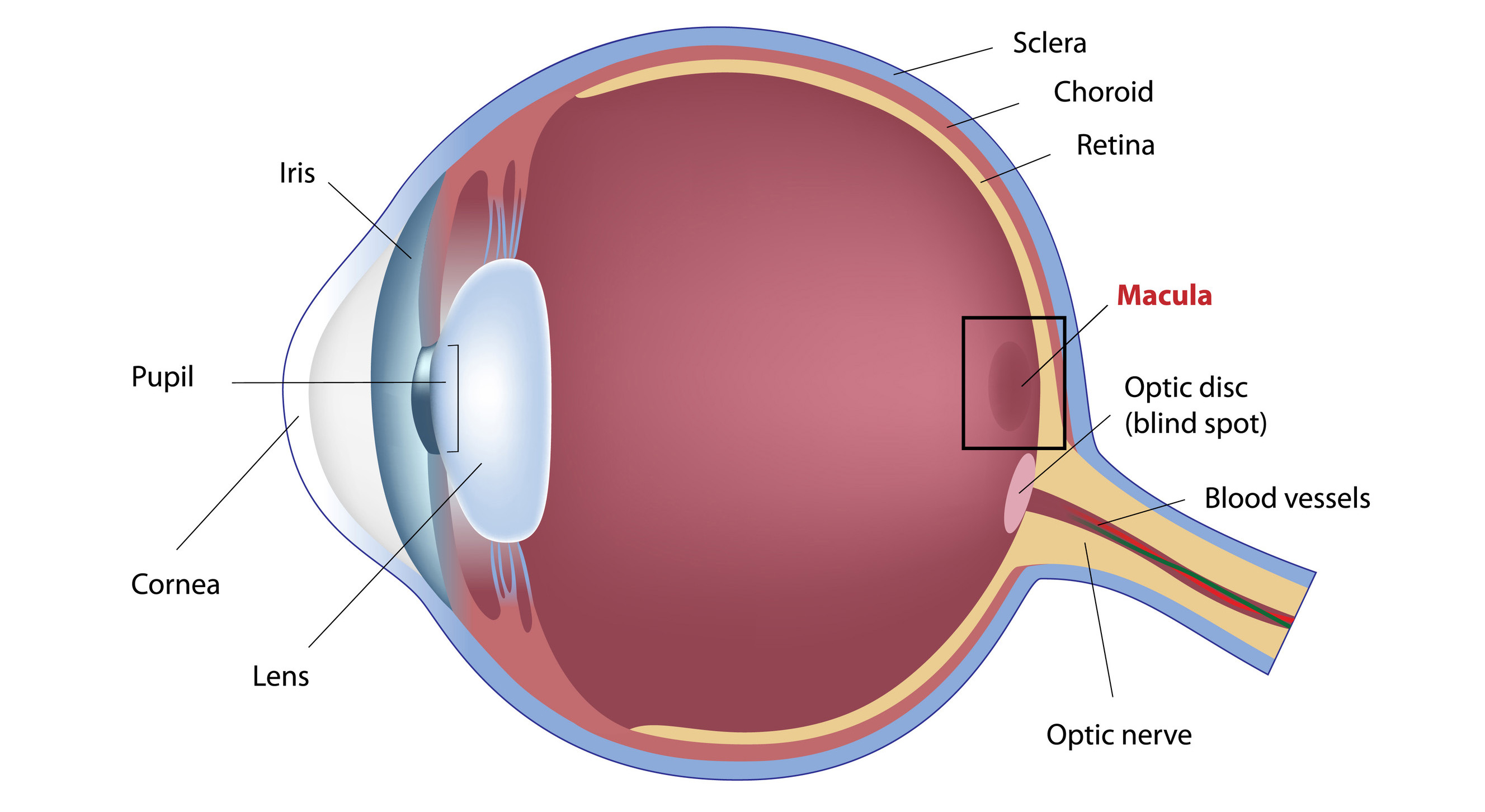
Eye health, often overlooked until problems arise, is essential for maintaining clear vision and preventing eye diseases, significantly impacting your quality of life.
A nutritious diet rich in essential nutrients, particularly lutein and zeaxanthin, can support your vision, as research indicates that these nutrients are crucial for eye health.
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a leading cause of vision loss in individuals over 50, affecting about 1 in 10 Americans. AMD is the primary cause of permanent blindness in developed countries, impacting around 170 million individuals globally. Symptoms may include distorted central vision.

An abundance of evidence suggests that a diet rich in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds not only promotes overall health but also supports vision health.
Lutein and zeaxanthin, potent antioxidants with significant health benefits, are vital for eye health. Lutein, a xanthophyll carotenoid, and zeaxanthin, another essential xanthophyll for eye health, are crucial for the human macula, providing distinct color to fruits and vegetables. As the body cannot produce carotenoids, they must be obtained through the diet, offering substantial support for vision health and reducing eye strain.
Both compounds serve as macular pigments, with lutein being highly concentrated in the eye's macula. Carotenoids accumulate in the retina and other eye structures, fulfilling various functions, including filtering harmful light and safeguarding photoreceptors from damage.
Carotenoids are also present in abundance in the brain.
Given that most people do not have a perfect diet that provides all necessary nutrients daily, and considering the crucial role clear vision plays in daily activities such as reading and driving, it is advisable to take measures to protect your eyesight.
Supplementing with lutein and zeaxanthin can help fill nutritional gaps in your diet.
Lutein and zeaxanthin supplements assist in supporting eye health and vision, lowering the risk of eye diseases.
Premium eye supplements offer a concentrated dose of these essential nutrients, ensuring adequate intake. Furthermore, these supplements have displayed benefits beyond vision health, including reducing inflammation and safeguarding brain health.
Dietary lutein and zeaxanthin are significantly concentrated in the human visual systems - the eye and brain - at levels about 1,000 times higher than elsewhere in the body. They constitute 80% to 90% of the carotenoids in the human eyes and are the predominant carotenoids in the neural retina and lens. They are also the primary carotenoids in the macular region of the retina.

Carotenoids act as a shield against harmful blue light, reducing eye strain and improving visual performance. Lutein and zeaxanthin contribute to eye health in numerous ways, some of which are not evaluated through standard eye examinations.
For example, contrast sensitivity, the ability to distinguish between objects and their backgrounds, is crucial in various situations, such as nighttime driving or in challenging weather conditions. Studies have indicated improvements in visual acuity and contrast sensitivity with lutein and zeaxanthin supplementation, although outcomes may differ based on study duration, ingredient amounts, and patient characteristics.
Research has demonstrated that a year of lutein supplementation led to enhanced glare and contrast sensitivity.
Macular pigment serves a structural role in vision as a blue light filter and potent antioxidant, supporting vision in the presence of potentially harmful light sources. Increasing macular pigment density has been associated with improved contrast sensitivity, reduced glare sensitivity, enhanced field of vision reaction times, and composite crash risk scores.
Studies have consistently shown visual benefits from boosting macular pigment density across diverse populations.
The Lutein Antioxidant Supplementation Trial (LAST) revealed that lutein increased macular pigment density, improved visual acuity, and enhanced contrast sensitivity.

Research indicates that lutein is the primary carotenoid in brain tissues and is linked to cognitive function in adults.
Elevated levels of circulating lutein have been associated with better cognitive performance in centenarians and other older populations.
Lutein's anti-inflammatory properties stimulate the production of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the brain, promoting neural plasticity and supporting learning and memory.

Lutein enhances memory and cognitive function, including spatial memory and reasoning ability. Spatial memory is crucial for locating objects and landmarks, while reasoning ability aids in understanding complex topics based on existing knowledge.
Studies have established a link between macular pigment density and prospective memory, with dietary factors associated with lutein intake potentially slowing age-related cognitive decline.
Lutein and zeaxanthin also support visual processing speed, essential for activities like sports and driving, as well as visual motor reaction time.
Research suggests that supplementing with lutein and zeaxanthin may aid in memory and learning as individuals age.
Carotenoids enhance executive functions such as decision-making, multitasking, and mental flexibility.

Lutein's ability to traverse the blood-brain barrier provides brain protection against oxidative stress, supporting neuroprotection and mitigating age-related cognitive decline.
Studies have shown that lutein supplementation enhances gray matter volume, particularly in the prefrontal cortex, and boosts functional connectivity in resting-state networks. Older adults with higher lutein levels also demonstrate increased white matter integrity.
Gray matter is crucial for processing information and cognitive functions, while white matter facilitates communication between brain regions and the rest of the body.
Various studies suggest that lutein and zeaxanthin intake supports brain activity and structures by crossing the blood-brain barrier.

Lutein is predominantly situated in the frontal cortex, visual cortex, and hippocampus, with higher concentrations in these brain regions compared to others.
Lutein's anti-inflammatory properties enhance the production of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), promoting neural plasticity and supporting memory and learning. Increased BDNF levels are associated with improved cognitive function and memory.
Lutein activates nuclear factor erythroid 2–related factor 2 (Nrf2), reducing oxidative stress and aiding in detoxification.
Studies like the Irish longitudinal study have underscored the connection between lutein and improved cognitive function in healthy older adults.
Nootropics, substances that aid the brain in generating new neural cells, may classify lutein and zeaxanthin supplements as potential nootropics.
Lutein and zeaxanthin assist in filtering out harmful blue light, protecting the eyes, in addition to their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.
Opt for eye supplements containing both lutein and zeaxanthin.
An ideal eye supplement may also incorporate vitamins C and E, and/or omega-3 fatty acids. Consuming the supplement with healthy fats enhances bioavailability.
Smokers should steer clear of supplements with beta-carotene.
Choose supplements devoid of allergens, artificial ingredients, GMOs, fillers, and additives like magnesium stearate or titanium dioxide. Organic supplements are preferred.

While lutein and zeaxanthin can be sourced from food, dietary intake of these compounds often falls below recommended levels. Focus on consuming whole foods rich in carotenoids such as:
Since carotenoids are fat-soluble, consume them with healthy fats to boost absorption. Opting for organic produce can significantly enhance nutrient absorption, like lutein, from your diet.
Lutein and zeaxanthin are essential nutrients crucial for eye health, vision clarity, and brain function, supporting memory and focus. While these nutrients can be obtained from food, they are often lacking in the typical diet. Hence, it is recommended to supplement with lutein and zeaxanthin to maintain eye and brain health.
Additionally, remember that exercise, ample sleep, and stress management are also key components of overall health.
Studies affirm the effectiveness of lutein and zeaxanthin in promoting vision and brain health.
Lutein and zeaxanthin, as essential components of macular pigment, are linked to improved vision, with many individuals experiencing enhanced vision upon increasing their lutein intake and boosting macular pigment density.
The timeframe for noticeable effects varies among individuals, with some experiencing rapid relief from eye strain due to the blue light and UV light-filtering properties of these nutrients.
Blueberries are not primary sources of lutein and zeaxanthin. For optimal intake, focus on kale, spinach, and yellow/orange vegetables like bell peppers and winter squash.